

By Monica Camacho
Missouri Grade Level Expectations for Grade 3:
Strand 3: Characteristics and Interactions of Living Organisms
3.D.: Plants and animals have different structures that serve similar functions necessary for the survival of the organism
3.D.a: Identify the major organs (roots, stems, flowers, leaves) and their functions in vascular plants (e.g., absorption, transport, reproduction
Knowledge Objective: Students will be able to observe how water travels in a plants stem by observing a colored dye traveling through a celery stalk.
Performance Objective: Students will be able to conduct an experiment by placing a celery stalk in dye. Students will use data and draw the outcome. Students will also measure how far the dye traveled up the celery stalk. Students will draw the level of the dye on a celery stalk picture.
Concept Introduction:
Students will understand that plants has parts that serve functions. A stem helps water move up to the flower in order for the flower to live. Students will watch the reaction of the dye to act as a visual of how water transports up the stem to the flower. By demonstrating with celery, students will understand that the stalk of the celery acts as the stem of a plant and that the stem carries water and nutrients from the ground to the other parts of the plant.

Materials needed for Activity:
1. leafy celery stalks
2. blue food coloring
3. clear tall cups
4. water
5. ruler
6. data sheet

Vocabulary:
Stem-Part of a plant that supports other parts, such as leaves, flowers, buds; part of a plant that carries water and nutrients from the ground to other plant parts.
Root-Underground part of a plant which serves to anchor the plant in place; also delivers water and nutrients from the ground to the stem.
Leaf-Lateral outgrowth from the stem whose primary function is food manufacturing.
Bud-An incompletely opened flower
Flower-Part of a plant that is usually colorful and protrudes from the stem; serves in reproduction.

History:
Plants are living things and have many of the same needs as humans. As plants grow, they need light, water, mineral nutrients, and air to live. Plants absorb water and mineral nutrients through the plant's vascular system. Plants need water and nutrients from the soil to survive. Plants take in water and mineral nutrients from their roots through their stems. When plants take in water from the ground, they are also getting some of the nutrients they need from the soil. A small part of the plants' nutrients comes from the soil. A large part of the plants' nutrients comes from air. The nutrients, which come from the soil, are dissolved in water and absorbed through a plants' roots.
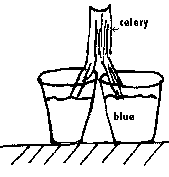
Activity (Exploration):
After learning about the parts and functions of a plant, the teacher will bring out a glass filled with blue-dyed water and a celery stalk. The teacher will ask the students, "If this piece of celery represents the stem of a plant, what will happen when it is placed in this glass of colored water?" Students will be in groups, each having a glass filled with blue colored water and a celery stalk. The students will test and observe how water is traveling up a celery stalk by peeling off a piece of the stalk to see where the water has traveled. The students will make a prediction of what would happen to the celery stalk by writing down their predictions on their data chart. Student will draw and measure the levels of the water every 30 minutes.
Data (Exploration):

Once the students have placed the celery in the colored water, they will write down their predictions of what will happen to the celery. The students will draw and measure the levels of the water every 30 minutes by recording their measurements on a data chart. The students will draw the level of the water on a celery stalk every 30 minutes throughout the day. Students will answer questions during and after the experiment and will share their results with the rest of the class.
Activity Enrichment (Application):
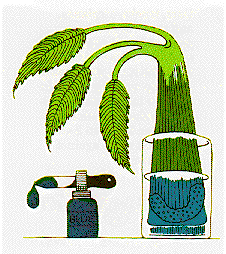
Can a carnation do the same effect like a celery stalk? Students will test a carnation with blue dye to see if the carnation will carry water up the stem to the flower. Students will record their findings on a data chart and draw a picture every 30 minutes after peeling off some of the stems layers. Students will measure with a ruler how far up the water has gone every 30 minutes.
Click on the arrow to view the student page or clink on each link below.
Student Page:
Exploration: celery data chart
Application: carnation data chart
Resources: